E-commerce
E-commerce, or electronic commerce, is like shopping online. Imagine a virtual mall where you browse for clothes, electronics, or anything else. You can compare prices, read reviews, and purchase with a few clicks. E-commerce lets stores reach customers worldwide, and you can shop from the comfort of your home.



Benefits of E-commerce
For Businesses
- Wider Reach: Sell to a global audience.
- Reduced Costs: Save on rent, staff, and marketing.
- Valuable Data: Gain customer insights to improve offerings.
- Streamlined Operations: Simplify inventory management.
- Faster Scalability: Easily grow your business.
For Consumers
- Convenience: Shop 24/7 from anywhere.
- Wider Selection: Find a greater variety of products.
- Comparison Shopping: Easily compare prices and features.
- Detailed Information: Access in-depth product descriptions and reviews.
- Multiple Payment Options: Choose your preferred payment method.



User Experience
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/E-commerceEcommerce UX is about creating a smooth online shopping journey. It's like having a well-organized store where everything's easy to find, so customers can buy what they want quickly and happily. This leads to more sales and loyal customers for your business.
Here are some key aspects of a great e-commerce UX:
Easy Navigation: A clear and organized website structure allows users to find products quickly.
High-Quality Product Information: Detailed descriptions, multiple images, and user reviews help users make informed decisions.
Successful Projects
Quality Customers
Trusted Partners
Why E-commerce is Imp?
E-commerce has become crucial for both businesses and consumers for several reasons:
-
Convenience: Shop anytime, anywhere with an internet connection. No need to travel or wait in line.
-
Wider Selection: Businesses can reach a global audience, and consumers have access to a much broader range of products.
-
Competitive Prices: Online stores often have lower overhead costs, leading to competitive pricing and frequent deals.
-
Information & Reviews: Easy access to product information, reviews, and comparisons to make informed decisions.
-
24/7 Availability: Unlike physical stores, online stores are always open, allowing for flexible shopping.

Evolution of E-commerce strategies
Ecommerce strategies have evolved from basic online storefronts in the 1990s to sophisticated omnichannel approaches in the present day. Early strategies focused on building trust and secure transactions, while the 2000s saw diversification with SEO and social commerce. The 2010s brought about a shift towards personalization and mobile optimization, alongside the integration of data analytics for targeted marketing. Present strategies prioritize sustainability and ethical practices, alongside the adoption of emerging technologies like AR, VR, and voice commerce to enhance the shopping experience. Overall, the evolution reflects a continuous effort to meet changing consumer expectations and leverage technological advancements for business growth.


Trends of E-commerce
Mobile Commerce (M-commerce): With the increasing use of smartphones, more consumers are shopping via mobile devices. E-commerce platforms are optimizing their websites and apps for seamless mobile experiences.
Voice Commerce: Voice assistants like Amazon’s Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri are shaping the way consumers shop. Voice commerce allows users to make purchases using voice commands, creating new opportunities for e-commerce businesses.
AI and Machine Learning: E-commerce platforms are leveraging AI and machine learning algorithms to personalize product recommendations, improve search functionality, and enhance customer service through chatbots.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies are being used to provide immersive shopping experiences, allowing customers to visualize products before making a purchase, particularly in industries like fashion, furniture, and home décor.
Social Commerce: Social media platforms are increasingly integrating e-commerce features, enabling businesses to sell products directly through their social profiles. Influencer marketing is also playing a significant role in driving sales on social platforms.
Subscription E-commerce: Subscription-based models are gaining popularity, offering convenience and cost savings to consumers while providing businesses with recurring revenue streams.
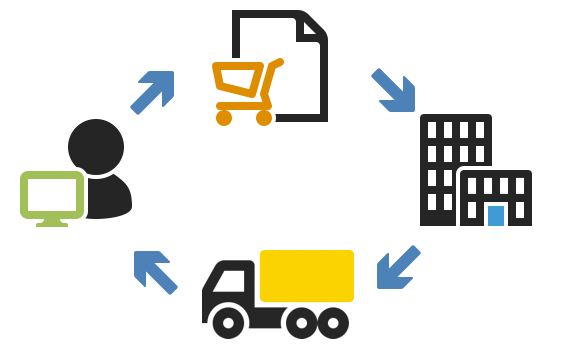
How does E-commerce work?
Businesses:
- Build an online store: This is their virtual storefront, often created using website builders or ecommerce platforms.
- List products: Businesses add details, descriptions, pictures, and set prices for their products.
- Customers browse: People visit the store using their devices, browsing products and adding them to a virtual shopping cart.
-
Consumers:
- Find products: They search online, using search engines or visiting specific stores.
- Research and compare: Customers browse listings, compare features and prices, and read reviews before buying.
- Add to cart and checkout: Once they decide, they add items to their virtual cart and proceed to checkout securely.
